Traverse Global v11.2 - Service Repair
Operations
Use the Operations function to define the operation process by pulling the tooling, machine group, labor type, and work center together. Drilling, painting, mixing, and packaging all describe typical internal operations. If the operation is internal, you can define the various related times involved in manufacturing. Within this function, you can define queue time, setup time, run time, wait time, and move time in terms of hours, minutes, and seconds. You can also use this function to set up a subcontracted operation.
Note: You can track actual setup and run times using the Production module.
There are two approaches to setting up internal operations. One method is to create very few operations and use them for a broad range of needs, resulting in a limited number of generic operations used for all processes, which makes the setup of operations much simpler and quicker. The other method is to create detailed operations, which makes each operation slightly different and more specifically addresses each unique operation within your environment.
There are four types of operations divided into two major types:
Internal operations are operations done in the plant and for which you usually incur labor or machine expense.
- Per Unit - Time is stated in the number of seconds, minutes, or hours to produce 1 unit. Example: 45 Seconds. This is the traditional way we've done it in the past.
- Run Rate - Time is not stated but selected as Seconds, Minutes, or Hours. The user enters the Quantity in the first field, not the time. Example 900 Units per Hour.
- Batch - Time is stated in terms of what it takes to process a batch. Batch size is stated in the Max Batch Qty field. Example 4 hours to produce 5000 kilos. This would it will take 4 hours to process 5000 kilos and, of course, 5000 would be set up in the Max Batch Qty. Setup is still setup, if setup says 1 hour, it's the time to set up each batch so you would add it to the time, thus, in this case it would actually take 5 hours to process 5000 kilos.
Subcontracted operations are operations done outside the plant by someone else. You define lead times, rather than run or setup times for subcontracted operations.
Note: It is possible to have an operation that can be done both internally or subcontracted depending on your capacity situation at this time the job is run.
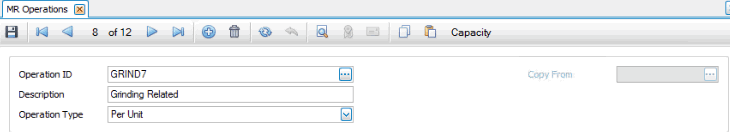
- Enter a new Operation ID. When you set up an operation for the first time, you can copy information from an existing operation to save time if the operations are similar. To do so, select an existing operation from the Copy From box. Information from the existing operation populates both tabs on the screen.
- Enter a Description for the operation.
- Select the Operation Type. See below for specifics regarding each operation type.

If you use Capacity Scheduling, a Capacity command button will be available on the toolbar. This allows you to maintain the capacity of the resource. The scheduling engine uses this capacity, and any capacity adjustment, for generating a capacity schedule. The Capacity button opens a Resources Detail screen, which is the Resources maintenance screen from the CS Setup and Maintenance menu with the Resource Type and ID fields disabled. See the Resources topic for more information.
Per Unit operations are generally processes with relatively low quantities and process time of more than a minute.
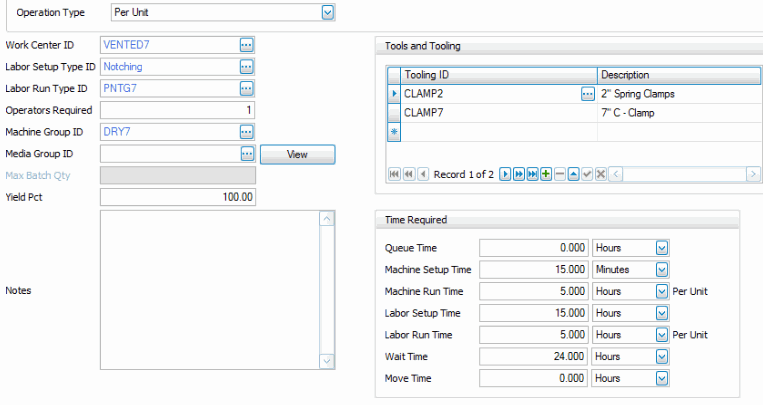
- Select the Work Center ID. The Work Center ID defines the work center where the work is to take place and the overhead rate for that given work center via the work center master. This field can be changed later, in the bill of material, if this operation is inserted into a bill of materials.
- Select the Labor Setup Type ID. The Labor Setup Type defines the labor skill required for the setup of this operation. This field can be changed later, in the bill of material, if this operation is inserted into a bill of materials.
- Select the Labor Run Type ID. The Labor Run Type defines the labor skill required to run this operation. This field can be changed later, in the bill of material, if this operation is inserted into a bill of materials.
- Enter the number of Operators Required to run the machine group for the run to be processed.
- Select the Machine Group. The Machine Group identifies the machine required for this process. It is an optional field. This field can be changed later, in the bill of material, if this operation is inserted into a bill of materials.
- Select the Media Group. The Media Group identifies the group of documents to be associated with this process. This is an optional field. Use the View button to view the documents.
- Enter the Yield Pct. The yield percentage indicates the efficiency of this process.
- Enter Notes. The notes field is an unlimited length field in which notes specific to this process can be entered. These notes pass through to the bills of material, and later appear on the production order worksheets.
- In the Tools and Tooling box, select the Tooling IDs needed to process this operation. The description of the Tooling ID is displayed.
- Enter the Queue Time and Units. The Queue time is the time we generally wait for the process to become available. It is not part of the BOM cost algorithm and is more or less an extra buffer time.
- Enter the Machine Setup Time and Units. The Machine Setup Time is the time required to set the machine up to run.
- Enter the Machine Run Rate and Units. The Machine Run Rate is the time required to process one piece or unit. For example; the CAD machine can drill and tap one unit in 7 minutes.
- Enter the Labor Setup Time and Units. The Labor Setup Time is the labor required to set up the process.
- Enter the Labor Run Rate and Units. The Labor Run Rate is the time required to process one piece or unit. For example; Bob can encase and package a unit in 5 minutes.
- Enter the Wait Time and Units. The Wait Time is the time required for the process to be ready to be used. It may be cooling, drying, solidifying, curing, etc. It is not part of the BOM costing algorithm.
- Enter the Move Time and Units. The Move Time is the time required for the materials to be moved to the next step. It is not part of the BOM costing algorithm.
Batch operations are generally operations that will run a specific number of units per batch.
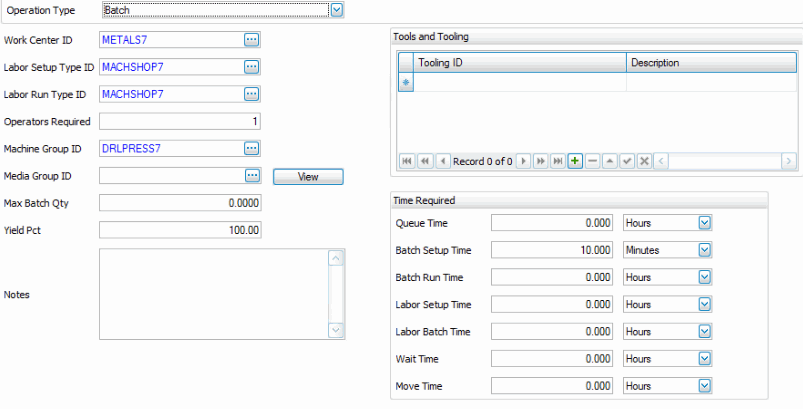
- Select the Work Center ID. The Work Center ID defines the work center where the work is to take place and the overhead rate for that given work center via the work center master. This field can be changed later, in the bill of material, if this operation is inserted into a bill of materials.
- Select the Labor Setup Type ID. The Labor Setup Type defines the labor skill required for the setup of this operation. This field can be changed later, in the bill of material, if this operation is inserted into a bill of materials.
- Select the Labor Run Type ID. The Labor Run Type defines the labor skill required to run this operation. This field can be changed later, in the bill of material, if this operation is inserted into a bill of materials.
- Enter the number of Operators Required to run the machine group for the run to be processed.
- Select the Machine Group. The Machine Group identifies the machine required for this process. It is an optional field. This field can be changed later, in the bill of material, if this operation is inserted into a bill of materials.
- Select the Media Group. The Media Group identifies the group of documents to be associated with this process. This is an optional field. Use the View button to view the documents.
- Enter the Max Batch Qty. The Max Batch Qty is the maximum size of the batch.
Knowing this and using the shown example of 1000, we know that an order for 2500 units would require 3 batches, as would an order for 3000 or 2001. The system will calculate time, not based on the quantity to be produced, but on the number of batches that quantity requires. The Time Required relates to the time to process a batch, not necessarily a given quantity.
The issue of unit of measure may come up as a significant issue but we should be able to assume the quantity generated by the product or “subassembly” this operation is used to produce, can drive this calculation.
For Example: We make chocolate candy bars. Telling the system we need 10,000 bars doesn't translate into a batch size of 10,000, but if the chocolate is set up as a “subassembly” called “chocolate batch mix”, the system will calculate how much “chocolate batch mix” is required to make 10,000 bars and that's the number we will need to use. This number is probably in pounds, ounces, kilograms, etc. but it's doesn't matter as long as the batch size is matched to the specific production process.
It would be highly unlikely that one product is produced in the same process in ounces and another is produced in pounds, but the system could handle that because each routing step in each bill could be unique. Also note that the Max Batch Qty is used in the setup time calculation as well as the run time.
- Enter the Yield Pct. The yield percentage indicates the efficiency of this process.
- Enter Notes. The notes field is an unlimited length field in which notes specific to this process can be entered. These notes pass through to the bills of material, and later appear on the production order worksheets.
- In the Tools and Tooling box, select the Tooling IDs needed to process this operation. The description of the Tooling ID is displayed.
- Enter the Queue Time and Units. The Queue time is the time we generally wait for the process to become available. It is not part of the BOM cost algorithm and is more or less an extra buffer time.
- Enter the Batch Setup Time and Units. The Batch Setup Time is the time required to set the batch up to run.
- Enter the Batch Run Time and Units. The batch run time is the time to process one batch, generally not including setup time. One might think of this, when thinking in terms of non-batch processes, as similar to machine time.
- Enter the Labor Setup Time and Units. The Labor Setup Time is the labor required to set up the process.
- Enter the Labor Batch Time and Units. The Labor Batch Time is the labor required in running the batch. This may be only a fraction of the batch run time because one laborer may maintain multiple batches or a minimal amount of labor is required during the batch process time. Generally the labor is far less than the total batch run time and may be set to zero.
- Enter the Wait Time and Units. The Wait Time is the time required for the process to be ready to be used. It may be cooling, drying, solidifying, curing, etc. It is not part of the BOM costing algorithm.
- Enter the Move Time and Units. The Move Time is the time required for the materials to be moved to the next step. It is not part of the BOM costing algorithm.
Run Rate operations are generally very fast high quantity operations. Many processes could be defined as Per Unit or Run Rate with essentially the same results. Note that many processes could be defined as Per Unit or Run Rate and although the setup within Traverse would be different, the results would be essentially the same. The advantage of a Run Rate operation is that one need not set the run times to extremely short times in terms of seconds or minutes, which can result in rounding problems.
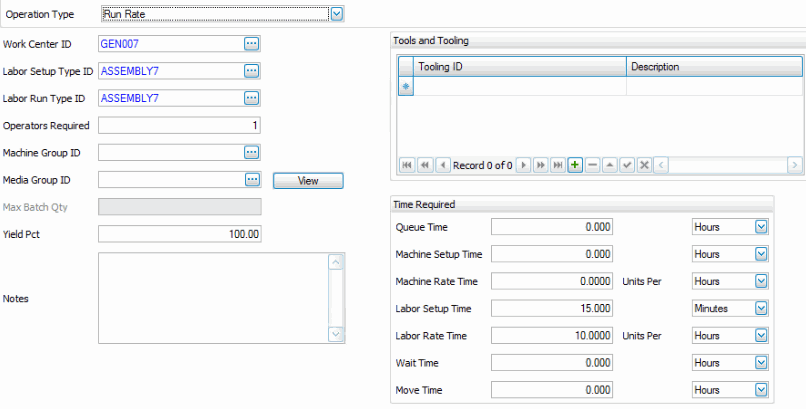
- Select the Work Center ID. The Work Center ID defines the work center where the work is to take place and the overhead rate for that given work center via the work center master. This field can be changed later, in the bill of material, if this operation is inserted into a bill of materials.
- Select the Labor Setup Type ID. The Labor Setup Type defines the labor skill required for the setup of this operation. This field can be changed later, in the bill of material, if this operation is inserted into a bill of materials.
- Select the Labor Run Type ID. The Labor Run Type defines the labor skill required to run this operation. This field can be changed later, in the bill of material, if this operation is inserted into a bill of materials.
- Enter the number of Operators Required to run the machine group for the run to be processed.
- Select the Machine Group. The Machine Group identifies the machine required for this process. It is an optional field. This field can be changed later, in the bill of material, if this operation is inserted into a bill of materials.
- Select the Media Group. The Media Group identifies the group of documents to be associated with this process. This is an optional field. Use the View button to view the documents.
- Enter the Yield Pct. The yield percentage indicates the efficiency of this process.
- Enter Notes. The notes field is an unlimited length field in which notes specific to this process can be entered. These notes pass through to the bills of material, and later appear on the production order worksheets.
- In the Tools and Tooling box, select the Tooling IDs needed to process this operation. The description of the Tooling ID is displayed.
- Enter the Queue Time and Units. The Queue time is the time we generally wait for the process to become available. It is not part of the BOM cost algorithm and is more or less an extra buffer time.
- Enter the Machine Setup Time and Units. The Machine Setup Time is the time required to set the machine up to run. This process can be costed.
- Enter the Machine Run Rate and Units. The Machine Rate is the number of pieces or units that can be run in a given time frame. For example, the label applicator can process 200 bottles per minute.
- Enter the Labor Setup Time and Units. The Labor Setup Time is the labor required to set up the process.
- Enter the Labor Run Rate and Units. The Labor Rate is the number of pieces or units that can be run for a given time frame. For example, Bob can paint 120 pieces per hour.
- Enter the Wait Time and Units. The Wait Time is the time required for the process to be ready to be used. It may be cooling, drying, solidifying, curing, etc. It is not part of the BOM costing algorithm.
- Enter the Move Time and Units. The Move Time is the time required for the materials to be moved to the next step. It is not part of the BOM costing algorithm.
Subcontracted operations are operations done outside the plant by someone else. You define lead times rather than run or setup times for subcontracted operations.
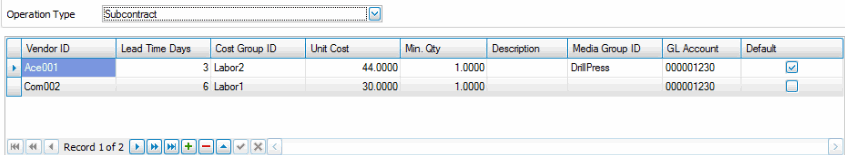
- Select the Vendor ID. The vendor ID is the AP vendor who performs the subcontracted service. All subcontractors must be set up in AP, although one does not need to process and invoice from them nor does the system automatically pay or create anything for them in regard to subcontracted operations they perform.
- Enter the Lead Time. The lead time represents the number of days required to send and receive back work from this vendor.
- Select the Cost Group. The Cost Group selected here will be used when this operation is inserted into a bill of material in breaking out the costs of that bill by cost group.
- Enter the Unit Cost. This field represents the cost per unit to process one unit. The field is optional. Because the vendor may perform a number of different operations at different costs, this field may or may not be meaningful.
- Enter the Min. Qty. This field indicates what the minimum quantity is for this vendor. The field is optional and is information only. Because the vendor may perform a number of different operations and have different minimums depending on the job, this field may or may not be meaningful.
- Enter the Description. The description field is a 30 character field, which describes the operation and which may include comments specific to this vendor.
- Select the Media Group. The Media Group identifies the group of documents to be associated with this process. This is an optional field.
- Select or enter the GL Account. Enter or select the GL expense account associated with this subcontracted operation when handled through the selected vendor from the drop-down list.
- Mark the Default check box if this is the default or preferred vendor amongst the vendors listed.
Editing an Operation
- Select an operation to edit from the Operation ID field.
- Edit the fields as necessary.
- Click the Save button, on the toolbar, to save any edits made.
Deleting an Operation
- Select an operation to delete from the Operation ID field.
- Click the Delete button, on the toolbar, to delete the selected operation.
- Click Yes at the "Are you sure you want to delete selected record(s)?" prompt.
Produce a Operations List
Use the Operations List function to view all the fields of the Operations master records.